Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O -type Schiff base complexes of tetravalent f-elements (M(IV) = Ce, Th, U, Np, and Pu) in solid state and in solution
-type Schiff base complexes of tetravalent f-elements (M(IV) = Ce, Th, U, Np, and Pu) in solid state and in solutionRadoske, T.*; Kloditz, R.*; Fichter, S.*; M rz, J.*; Kaden, P.*; Patzschke, M.*; Schmidt, M.*; Stumpf, T.*; Walter, O.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
rz, J.*; Kaden, P.*; Patzschke, M.*; Schmidt, M.*; Stumpf, T.*; Walter, O.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 49(48), p.17559 - 17570, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.17(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Wu, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Miller, C. J.*; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science; Water Research & Technology, 5(8), p.1400 - 1411, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:32.59(Engineering, Environmental)In this study, the distributions of iron and phosphorus species in a 1.25 m pilot scale submerged membrane bioreactor dosed with Fe(II) salts to either the membrane chamber or the 1st anoxic chamber were determined using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) at the iron and phosphorus K-edges. Significant differences in the distribution of Fe species were evident at the commencement of dosing depending on the chamber to which Fe(II) was dosed though these differences were much less distinct by the time steady state conditions were achieved. Both the co-precipitation of P with Fe and adsorption of phosphorus to iron oxides play important roles with regard to the removal of phosphorus from the MBR supernatant with the results of this work suggesting that P removal via formation of Fe(III)-phosphate mineral species is preferred if Fe(II) is dosed to the membrane chamber rather than the 1st anoxic chamber.
pilot scale submerged membrane bioreactor dosed with Fe(II) salts to either the membrane chamber or the 1st anoxic chamber were determined using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) at the iron and phosphorus K-edges. Significant differences in the distribution of Fe species were evident at the commencement of dosing depending on the chamber to which Fe(II) was dosed though these differences were much less distinct by the time steady state conditions were achieved. Both the co-precipitation of P with Fe and adsorption of phosphorus to iron oxides play important roles with regard to the removal of phosphorus from the MBR supernatant with the results of this work suggesting that P removal via formation of Fe(III)-phosphate mineral species is preferred if Fe(II) is dosed to the membrane chamber rather than the 1st anoxic chamber.
Schwehr, K. A.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Merchel, S.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Zhang, S.*; Xu, C.*; Li, H.-P.*; Ho, Y.-F.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Santschi, P. H.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 497-498, p.671 - 678, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:38.73(Environmental Sciences)A new, accurate and simple pH-dependent solvent extraction method combined with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) measurement for  I/
I/ I isotopes and iodine speciation (iodide, iodate, and organo-I) quantification in liquids of any ionic strength has been developed. We then validated the AMS method for activity concentration measurements with a recently developed gas chromatography mass spectrometry method for
I isotopes and iodine speciation (iodide, iodate, and organo-I) quantification in liquids of any ionic strength has been developed. We then validated the AMS method for activity concentration measurements with a recently developed gas chromatography mass spectrometry method for  I concentrations of 1 Bq/L or higher. This technique was applied to
I concentrations of 1 Bq/L or higher. This technique was applied to  I-contaminated groundwater from the Savannah River Site, USA, and demonstrated changes of
I-contaminated groundwater from the Savannah River Site, USA, and demonstrated changes of  I and
I and  I concentrations and speciation along a pH, redox potential, and organic carbon gradient. The data suggest that
I concentrations and speciation along a pH, redox potential, and organic carbon gradient. The data suggest that  I/
I/ I and species distribution is strongly pH dependent. The new method can now be applied to a wide range of chemically-diverse aquatic systems, including uncontaminated environments.
I and species distribution is strongly pH dependent. The new method can now be applied to a wide range of chemically-diverse aquatic systems, including uncontaminated environments.
Arisaka, Makoto; Kimura, Takaumi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yoshida, Zenko
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1307 - 1311, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.64(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Kitamura, Akira; *
JNC TN8400 2001-009, 54 Pages, 2001/01
Spectroscopic measurements of neodymium(III) and samarium(III) were carried out by spectrophotometer and laser-induced photoacoustic spectroscopic (LPAS) system for the investigation of the detection limit of both systems. The absorption spectra and photoacoustic spectra of Nd and Sm
and Sm were obtained with varying the concentration of the ions from 2
were obtained with varying the concentration of the ions from 2 10
10 to 2
to 2 10
10 mol
mol dm
dm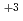 . The absorption spectrum of Nd
. The absorption spectrum of Nd was also determined by a special spectrophotometer, of which the measurement cell was set in a glove box filled with inert nitrogen gas. For the comparison with these photoacoustic and absorption spectra, the absorption spectra of Nd
was also determined by a special spectrophotometer, of which the measurement cell was set in a glove box filled with inert nitrogen gas. For the comparison with these photoacoustic and absorption spectra, the absorption spectra of Nd and Sm
and Sm were determined by an usual spectrophotometer with the light-path lengths of 1 cm and 10 cm. The detection limit of the photoacoustic measurement was reported much lower than that of absorbance measurement by several researchers. However, the present study was concluded that the detection limit of photoacoustic measurement with the present LPAS system was similar to that of absorbance measurement with the light-path length of 10 cm. The detection limits of neptunium(IV,V) were estimated and the possibility of the speciation of neptunium(IV) was discussed from the results of the present study.
were determined by an usual spectrophotometer with the light-path lengths of 1 cm and 10 cm. The detection limit of the photoacoustic measurement was reported much lower than that of absorbance measurement by several researchers. However, the present study was concluded that the detection limit of photoacoustic measurement with the present LPAS system was similar to that of absorbance measurement with the light-path length of 10 cm. The detection limits of neptunium(IV,V) were estimated and the possibility of the speciation of neptunium(IV) was discussed from the results of the present study.
*; Akatsuka, Hiroshi*; *; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; *; *;
JNC TY9400 2000-009, 41 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-065, 379 Pages, 1999/10
A database for diffusivity for a data setting of effective diffusion coefficients in rock matrices in the second progress report, was developed. In this database, 3 kinds of diffusion coefficients: effective diffusion coefficient (De), apparent diffusion coefficient (Da) and free water diffusion coefficient (Do) were treated. The database, based on literatures published between 1980 and 1998, was developed considering the following points. (1)Since Japanese geological environment is focused in the second progress report, data for diffusion are collected focused on Japanese major rocks. (2)Although 22 elements are considered to be important in performance assessment for geological disposal, all elements and aquatic tracers are treated in this database development considering general purpose. (3)Since limestone, which belongs to sedimentary rock, can become one of the natural resources and is inappropriate as a host rock, it is omitted in this database development. Rock was categorized into 4 kinds of rocks; acid crystalline rock, alkaline crystalline rock, scdimentaly rock (argillaceous/tuffaceous rock) and sedimentary rock (psammitic rock/sandy stone) from the viewpoint of geology and mass transport. In addition, rocks around neutrality among crystalline rock were categorized into the alkaline crystalline rock in this database. The database is composed of sub-databases for 4 kinds of rocks. Furthermore, the sub-databases for 4 kinds of the rocks are composed of databases to individual elements, in which totally, 24 items such as species, rock name, diffusion coefficients (De, Da, Do), obtained conditions (method, porewater, pH, Eh, temperature, atmosphere, etc.), etc. are input. As a result of literature survey, for De values for acid crystalline rock, totally, 207 data for 18 elements and one tracer (hydrocarbon) have been reported and all data were for granitic rocks such as granite, granodiorite and biotitic granite. For alkaline crystallinc rock, ...
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-062, 16 Pages, 1999/10
Effective diffusion coefficients (De) for Ni , Sm
, Sm , Am
, Am and SeO
and SeO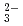 were measured as a function of the ionic charge of diffusion species to quantitatively evaluate the effect of ionic charge in compacted bentonite. The De measurements for Ni
were measured as a function of the ionic charge of diffusion species to quantitatively evaluate the effect of ionic charge in compacted bentonite. The De measurements for Ni and Sm
and Sm were carried out for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg
were carried out for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with a simulated porewater condition of pH5
with a simulated porewater condition of pH5 6 by through-diffusion method. The De values for SeO
6 by through-diffusion method. The De values for SeO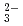 were measured for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg
were measured for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with a simulated porewater condition of pH11. The De measurements for Am
with a simulated porewater condition of pH11. The De measurements for Am were carried out for the dry densities of 0.8, 1.4 and l.8 Mg
were carried out for the dry densities of 0.8, 1.4 and l.8 Mg m
m with a porewater condition of pH2 in order to check cation exclusion. Sodium bentonite, Kunigel-V1 was used for those measurements. For the measurements of Am, H-typed Kunigel-V1 which interlayer ion (Na
with a porewater condition of pH2 in order to check cation exclusion. Sodium bentonite, Kunigel-V1 was used for those measurements. For the measurements of Am, H-typed Kunigel-V1 which interlayer ion (Na ) was exchanged with H
) was exchanged with H was used, because the experiments are carried out for a low pH range. The order of obtained De values was Sm
was used, because the experiments are carried out for a low pH range. The order of obtained De values was Sm
 Ni
Ni
 Am
Am
 SeO
SeO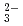 . These De values were compared to those reported to date. Consequently, the order of De values was Cs
. These De values were compared to those reported to date. Consequently, the order of De values was Cs
 Sm
Sm
 HTO
HTO  Ni
Ni
 anions (I
anions (I , Cl
, Cl , CO
, CO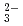 , SeO
, SeO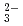 TcO
TcO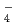 , NpO
, NpO CO
CO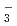 , UO
, UO (CO
(CO )
)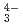 ), showing a tendency of cations
), showing a tendency of cations  HTO
HTO  anions. Only the De values of Am
anions. Only the De values of Am were approximately the same degree as those of anions. The reason that the De of Ni
were approximately the same degree as those of anions. The reason that the De of Ni was lower than that of HTO may be because the free water diffusion coefficient (Do) of Ni
was lower than that of HTO may be because the free water diffusion coefficient (Do) of Ni is about 1/3 of that of HTO. The cause that the De of Am
is about 1/3 of that of HTO. The cause that the De of Am was approximately the same degee as those of anions may be because the Do of Am
was approximately the same degee as those of anions may be because the Do of Am is about 1/3 of that of HTO and that Am
is about 1/3 of that of HTO and that Am was electrostatically repulsed from the surface of bentonite by cation exclusion. The formation factors (FF), calculated normalizing Do, were in the ...
was electrostatically repulsed from the surface of bentonite by cation exclusion. The formation factors (FF), calculated normalizing Do, were in the ...
Oda, Chie; Arthur, R. C,*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Shibata, Masahiro; Yui, Mikazu; Neyama, Atsushi*
JNC TN8400 99-079, 287 Pages, 1999/09
Two thermodynamic databases for geochemical calculations supporting research and development on geological disposal concepts for high level radioactive waste are described in this report. One, SPRONS.JNC, is compatible with thermodynamic relations comprising the SUPCRT model and software, which permits calculation of the standard molal and partial molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species and reactions from 1 to 5000 bars and 0 to 1000 C. This database includes standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard molal entropies and volumes, and Maier-Kelly heat capacity coefficients at the reference pressure (1 bar) and temperature (25
C. This database includes standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard molal entropies and volumes, and Maier-Kelly heat capacity coefficients at the reference pressure (1 bar) and temperature (25 C) for 195 minerals and 16 gases. It also includes standard partial molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard partial molal entropies, and Helgeson, Kirkham and Flowers (HKF) equation-of-state coefficients at the reference pressure and temperature for 1147 inorganic and organic aqueous ions and complexes. SPRONS.JNC extends similar databases described elsewhere by incorporating new and revised data published in the peer-reviewed literature since 1991. The other database, PHREEQE.JNC, is compatible with the PHREEQE series of geochemical modeling codes. It includes equilibrium constants at 25
C) for 195 minerals and 16 gases. It also includes standard partial molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard partial molal entropies, and Helgeson, Kirkham and Flowers (HKF) equation-of-state coefficients at the reference pressure and temperature for 1147 inorganic and organic aqueous ions and complexes. SPRONS.JNC extends similar databases described elsewhere by incorporating new and revised data published in the peer-reviewed literature since 1991. The other database, PHREEQE.JNC, is compatible with the PHREEQE series of geochemical modeling codes. It includes equilibrium constants at 25 C and 1 bar for mineral-dissolution, gas-solubility, aqueous-association and oxidation-reduction reactions. Reaction enthalpies, or coefficients in an empirical log K(T) function, are also included in this database, which permits calculation of equilibrium constants between 0 and 100
C and 1 bar for mineral-dissolution, gas-solubility, aqueous-association and oxidation-reduction reactions. Reaction enthalpies, or coefficients in an empirical log K(T) function, are also included in this database, which permits calculation of equilibrium constants between 0 and 100 C at 1 bar. All equilibrium constants, reaction enthalpies, and logK(T) coefficients in PHREEQE.JNC are calculated usig SUPCRT and SPRONS.JNC, which ensures that these two databases are mutually consistent. They are also internally consistent insofar as all the data are compatible with basic thermodynamic definitions and functional relations in the SUPCRT ...
C at 1 bar. All equilibrium constants, reaction enthalpies, and logK(T) coefficients in PHREEQE.JNC are calculated usig SUPCRT and SPRONS.JNC, which ensures that these two databases are mutually consistent. They are also internally consistent insofar as all the data are compatible with basic thermodynamic definitions and functional relations in the SUPCRT ...
Kihara, Sorin*; Yoshida, Zenko; Aoyagi, Hisao; Maeda, Koji*; Shirai, Osamu; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Yumi*
Pure and Applied Chemistry, 71(9), p.1771 - 1807, 1999/09
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:83.55(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English

 and AnO
and AnO
 Species in Geologic Environments
Species in Geologic EnvironmentsChoppin, G. R.*; Bronikowski, M.*; Chen, J.*; Byegard, J.*; Rai, D.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-012, 155 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of pentavalent and hexavalent actinide species (AnO and AnO
and AnO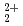 ) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO
) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO and AnO
and AnO
 , redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
, redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Takeda, Seiji
JAERI-Data/Code 99-001, 74 Pages, 1999/01
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kimura, Takaumi; Kato, Yoshiharu; *; *
Radiochimica Acta, 82, p.227 - 232, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Haruo
PNC TN8410 97-075, 29 Pages, 1997/04
In the performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in Japan, redox condition in deep geological environment is considered to be reducing, and Se is one of the important redox sensitive elements. However, no studies on diffusion of Se in bentonite under reducing conditions have been reported yet. This paper describes the results of apparent diffusion coefficients of Se in compacted sodium bentonite obtained as a function of bentonite density under reducing conditions and discusses its diffusion behaviour. Apparent diffusion coefficients of Se in compacted sodium bentonite, Kunigel V1 (constituent montmorillonite 46  49wt%), were obtained in a range of dry densities of bentonite, 800
49wt%), were obtained in a range of dry densities of bentonite, 800  1800 kg
1800 kg m
m under reducing conditions (Eh vs. SHE -373
under reducing conditions (Eh vs. SHE -373  -363mV) at room temperature (23.6
-363mV) at room temperature (23.6  23.7
23.7 C) by in-diffusion method. All the experiments were carried out in an N
C) by in-diffusion method. All the experiments were carried out in an N -atmospheric glove box (O
-atmospheric glove box (O
 1ppm) and the reducing conditions of the porewater were maintained by continuous contact between compacted bentonite and reducing solution including 5.7
1ppm) and the reducing conditions of the porewater were maintained by continuous contact between compacted bentonite and reducing solution including 5.7  10
10 M-Na
M-Na S
S O
O through a sintered metal filter. The Eh of reducing solution was continuously monitored. Furthermore, a through-diffusion experiment of Na
through a sintered metal filter. The Eh of reducing solution was continuously monitored. Furthermore, a through-diffusion experiment of Na S
S O
O was also carried out at a dry density, 1800 kg
was also carried out at a dry density, 1800 kg m
m in order to check the reducing condition of the porewater. The Eh in the measurement cell was confirmed to be the same as that in the tracer cell. The apparent diffusion coefficients of Se were in the range, 6.1
in order to check the reducing condition of the porewater. The Eh in the measurement cell was confirmed to be the same as that in the tracer cell. The apparent diffusion coefficients of Se were in the range, 6.1 10
10
 4.3
4.3 10
10 m
m
 s
s and showed a tendency of slight decrease with increasing dry density of bentonite. The dominant species of Se in the porewater under reducing conditions is predicted to be HSe
and showed a tendency of slight decrease with increasing dry density of bentonite. The dominant species of Se in the porewater under reducing conditions is predicted to be HSe , and the apparent diffusion coefficients of HSe
, and the apparent diffusion coefficients of HSe in the bentonite were approximately the same as those of TcO
in the bentonite were approximately the same as those of TcO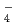 ...
...
 Co adsorbed on sand
Co adsorbed on sandTanaka, Tadao; Muraoka, Susumu
Radioisotopes, 45(12), p.753 - 760, 1996/12
no abstracts in English
Takebe, Shinichi; Mukai, Masayuki; Komiya, Tomokazu; Kamiyama, Hideo
JAERI-M 92-205, 19 Pages, 1993/01
no abstracts in English
; ; ;
Nihon Kagakkai-Shi, 8, p.1249 - 1256, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
; ;
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 49(12), p.3584 - 3588, 1976/12
Times Cited Count:5no abstracts in English
 fullerene as the adsorbent of Cs
fullerene as the adsorbent of CsKobayashi, Takanori; Yokoyama, Keiichi
no journal, ,
We have a plan for isotope separation of  Cs using the difference of rotational constants of CsI. In the plan, the adsorbent which can adsorb Cs species-selectively is desirable for the recovery of
Cs using the difference of rotational constants of CsI. In the plan, the adsorbent which can adsorb Cs species-selectively is desirable for the recovery of  Cs after isotope-selective dissociation process of CsI. Paying attention to the difference of the chemical nature of CsI and Cs, fullerenes would be expected to be desirable as the adsorptive material. To confirm the idea, we have calculated the adsorption energy of Cs, CsI etc. to C
Cs after isotope-selective dissociation process of CsI. Paying attention to the difference of the chemical nature of CsI and Cs, fullerenes would be expected to be desirable as the adsorptive material. To confirm the idea, we have calculated the adsorption energy of Cs, CsI etc. to C fullerene using quantum chemistry calculation. We have also calculated the adsorption energy of a cluster model of illite, a kind of minerals which exists in soil and is known as a Cs
fullerene using quantum chemistry calculation. We have also calculated the adsorption energy of a cluster model of illite, a kind of minerals which exists in soil and is known as a Cs adsorbent. The results show that C
adsorbent. The results show that C fullerene would be suitable to adsorb Cs atom in many CsI molecules. In the paper, we will discuss the thermochemical stability of the adducts.
fullerene would be suitable to adsorb Cs atom in many CsI molecules. In the paper, we will discuss the thermochemical stability of the adducts.